Tutankhamun’s Pectoral: A Cosmic Artifact
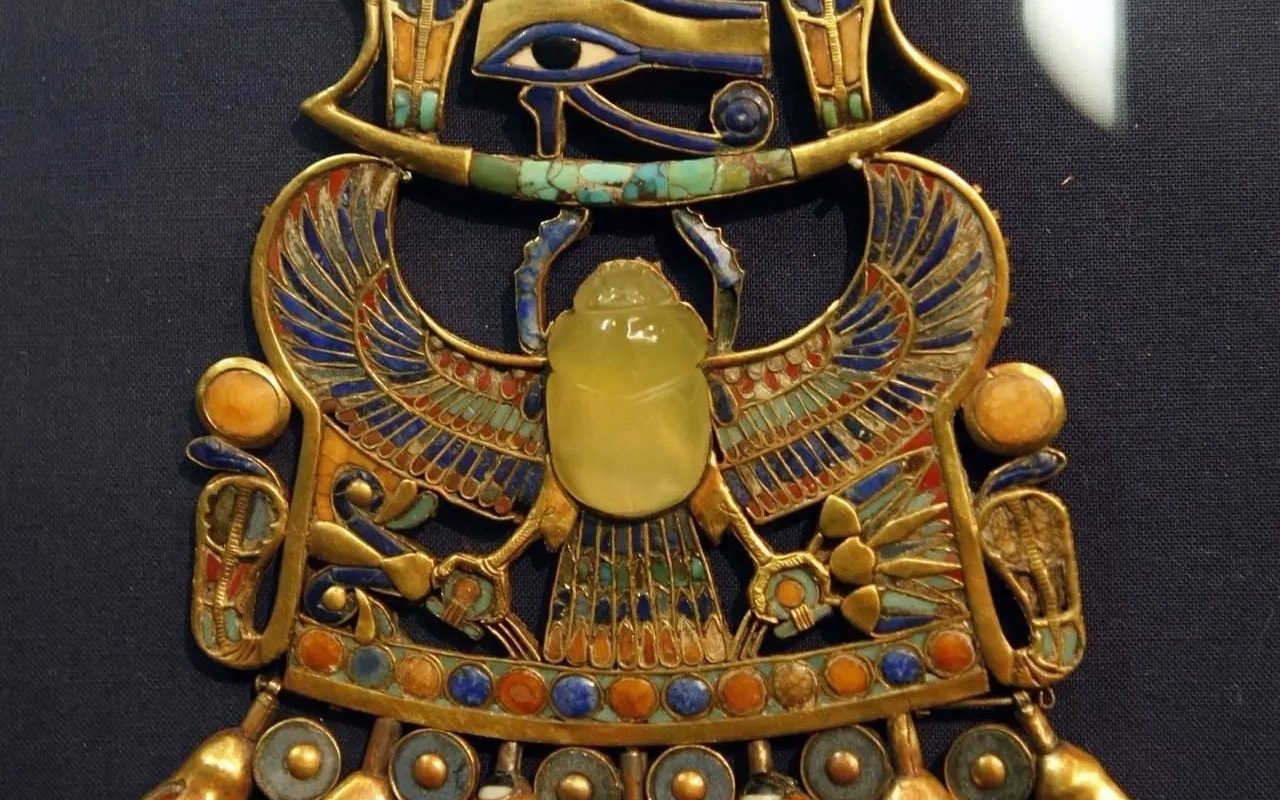
One of the most remarkable artifacts linking the ancient world with cosmic phenomena lies in the tomb of Pharaoh Tutankhamun. His pectoral, a chest ornament, holds at its center a scarab made from a rare yellow-green glass. Today, scientists identify it as Libyan Desert Glass.
The Origin of Libyan Desert Glass
This glass was not created by humans. Instead, studies show it formed nearly 28 million years ago. At that time, a massive meteorite or comet exploded over the Sahara Desert. The blast generated extreme heat, reaching more than 1,600 °C. As a result, desert sand melted into glass.
This material occurs only in a specific region. Moreover, it is considered one of the oldest natural glasses on Earth.
Symbolism for the Ancient Egyptians
For the Egyptians, the scarab symbolized rebirth, immortality, and the protective power of the sun god Ra.
The design of the pectoral also includes the Eye of Horus (Udjat), a symbol of protection against evil. Therefore, the jewel combined both religious and cosmic meanings in a single masterpiece.
Scientific and Mystical Interpretations
- Scientists view the glass as natural proof of ancient cosmic impacts on Earth.
- Alternative theories suggest the Egyptians understood cosmic energy and intentionally used materials of celestial origin.
A Legacy for Our Time
Today, the scarab in Tutankhamun’s pectoral is not only a masterpiece of art and religion. It is also a unique geological specimen showing the close connection between Earth and the cosmos. In fact, it represents one of the rare moments when an ancient civilization used a material born beyond our planet.